Methods of Selection
Methods of Selection
Employees
are the most significant asset for any organization since they have a direct
impact on the organization's performance. As a result, the development of an
organization is dependent on effective human resource management. Selection and
recruiting are essential components of human resource management strategies
used by organizations to develop and improve personnel capabilities in order to
achieve both individual and organizational goals (Abbas,
Shah and Othman, 2021).
The process
of selecting candidates with the necessary qualifications to fill positions within
the organization is known as selection. Selection entails much more than simply
selecting the finest applicant. It is an attempt to establish a fine balance
between what the candidate is capable of and desires to perform and what the
company expects. The selection of the appropriate workers is critical for three
reasons: performance, cost, and legal obligations. Selection prerequisites and
Requirements (Gupta
and Kumar, 2014);
I. Choosing personnel with necessary qualifications
ii. Aligning
job needs with candidate profiles
iii. Using
a variety of methods and approaches to identify the best qualified applicant
for work success
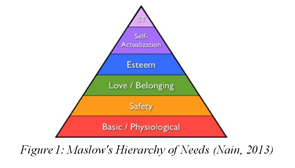
For better
understanding, the Selection Process is shown in the following diagram in Figure
1.
Success of a selection process is enhanced by restricting options for input from individuals with lesser qualifications to the job criteria. The entity in charge of carrying out the selection process in normally considered as a manager or a human resources department (Muscalu, 2015).
In the last
five years or more, there has been a growing interest in the literature about
comparisons of employee selection procedures in various European countries. A
book on recruitment released by the IPM in their European Management Guides
series in 1990, and a special issue of the European review of applied
psychology (ERAP) in 1991, are two of the most well-known examples. The ERAP
(1991) reports came from six different European countries: France, Germany, the
United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Norway, and Spain
As an
example, in these books the editor came to the realization that there were
significant differences in the procedures utilized in different nations, as
well as in other areas such as assessor training and qualifications and the
theoretical approach to selection concerns. According to the studies,
references and recommendations were far more common in the United Kingdom,
followed by the Netherlands, and much less common in Germany and France
Moving
forward, a candidate’s ability difference may have been eliminated as a result
of the hiring organization's selection methods. In conclusion, given that
Breaugh and Mann investigated for ability differences on new employees rather
than job seekers, but it was unclear what conclusions may be drawn from their
findings (Breaugh
and Starke, 2000).
Rynes and
Boudreau (1986) investigated 145 corporations' college recruiting programs.
Among the problems they explored were the factors that influenced the
companies' college decision. According to Rynes and Boudreau, the variables
assigned the most weight were a college's reputation in essential skill areas,
the institution's overall reputation, and the performance of past employees
from the school. They discovered that experienced hires were regarded more
highly in terms of their technical capabilities, interpersonal skills, work
expectations realistically, and chance of success on the job. New college
graduates were rated higher for their eagerness to learn new things (Breaugh
and Starke, 2000).
Moving on to
another application scenario, this particular research aimed at how applicants
react to 10 prevalent selection processes in China. Using a sample of 294
graduates, researchers discovered that work sample exams, interviews, and
written ability tests were highly regarded by Chinese candidates, but Guanxi and
graphology were seen as the least favored selection procedures. On all seven
procedural dimensions tested, Guanxi was rated as much less fair than the
others. These data imply that Guanxi as an informal selection route may
compromise the fairness of Chinese personnel selection. The implications for
the design of selection procedures in Chinese organizations were examined, as
well as the implications for future study into applicant reactions (Applicant Reactions to Selection Methods in China - Liu
- 2016 - International Journal of Selection and Assessment - Wiley Online Library,
no date).
To conclude
with, employer decisions on staff selection are critical to the running of
companies and the results that are important to individuals, organizations, and
society. The few studies that have looked at employer judgments concerning
selection processes discover a significant range in both the methodologies and
the amount to which selection is used in organizations(Wilk
and Cappelli, 2003).
References
·
Abbas, S.I.,
Shah, M.H. and Othman, Y.H. (2021) ‘Critical Review of Recruitment and Selection
Methods: Understanding the Current Practices’, Annals of Contemporary
Developments in Management & HR (ACDMHR), 3(3), pp. 46–52.
doi:10.33166/ACDMHR.2021.03.005.
·
Applicant Reactions to Selection Methods in China - Liu -
2016 - International Journal of Selection and Assessment - Wiley Online Library (no date).
Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ijsa.12148
(Accessed: 22 April 2022).
·
Breaugh, J.A. and Starke, M. (2000) ‘Research on Employee
Recruitment: So Many Studies, So Many Remaining Questions’, Journal of
Management, 26(3), pp. 405–434. doi:10.1177/014920630002600303.
·
Gupta, A. and Kumar, S. (2014) ‘A Study On Recruitment &
Selection Process With Reference’. doi:10.13140/2.1.2424.0320.
·
Muscalu,
E., 2015. Sources of Human Resources. Management and Economics, 3(79),
pp. 351-359.
· Shackleton, V. & Newell , S., 1994. European Management Selection: Methods: A Comparison of Five Countries. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 2(2), pp. 91-102.
·
Wilk, S.L. and Cappelli, P. (2003) ‘UNDERSTANDING THE
DETERMINANTS OF EMPLOYER USE OF SELECTION METHODS’, Personnel Psychology,
56(1), pp. 103–124. doi:10.1111/j.1744-6570.2003.tb00145.x.


Useful info, here is a list of some of the definitions from different about selection process (Vulpen, 2022):
ReplyDeleteEmployee selection is a process of putting a right applicant on a right job.
Selection of an employee is a process of choosing the applicants, who have the qualifications to fill the vacant job in an organization.
Selection is a process of identifying and hiring the applicants for filling the vacancies in an organization.
Employee selection is a process of matching organization’s requirements with the skills and the qualifications of individuals.